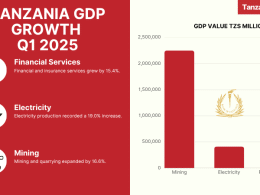
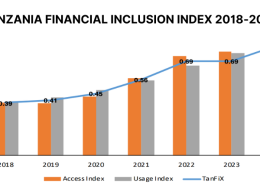
On 6th December 2018, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has published its latest Financial System Stability Assessment for Tanzania, based on the work of the Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) mission that visited the Country in April-May 2018.
In its summary, the IMF Executive Board reminded that Economic growth in Tanzania has been relatively strong in the past decade.
Prudent macroeconomic policies and consecutive Fund programs contributed to low inflation and contained public sector debt.
However, more recently a slowdown in economic momentum has emerged. Difficulties with fiscal management have led to a build-up of expenditure arrears, which contributed to a higher level of nonperforming loans.
Although the Tanzania authorities have strengthened financial prudential regulations and initiated a transition of the monetary framework toward an interest-rate based operating target, financial stability challenges could be significant.
Banks’ asset quality has deteriorated in recent years and provisioning needs have increased. Credit growth has fallen precipitously, corporate debt loads have risen, and their cash flows are weak.
Meanwhile, the dollarization of bank balance-sheets could create liquidity pressures under adverse shock scenarios.
Vulnerabilities could amplify the impact of external and domestic shocks, including from tighter global financial conditions, lower trading partner growth, prolongation of domestic economic uncertainties, and delays in addressing difficulties related to fiscal management.
This is why the IMF Executive Board advocates measures to reduce nonperforming loans and increase provisioning and buffers to manage liquidity, credit, and concentration risks.
These measures should be complemented by strengthening banking supervision and problem bank oversight.
In addition, continued macroeconomic stability, an improved business environment, better execution of fiscal policy and resolution of government payment arrears would help address financial sector vulnerabilities and risks.
In January this year, the IMF completed the 7th and last review of Tanzania’s economic performance, indicating that its outlook is subject to emerging risks.