The Bank of Tanzania (BOT) and Financial Sector Deepening Tanzania (FSDT) released a case study on May 16, 2025, detailing the development and impact of the Tanzania Instant Payment System (TIPS), aimed at building an inclusive and interoperable digital payments ecosystem
By the end of 2024, the Tanzania Instant Payment System (TIPS) had processed 453.7 million interoperable retail transactions worth TZS 29.9 trillion.
TIPS is a national real-time payment switch developed and operated by BOT to facilitate instant, low-value digital transactions between digital financial services providers, including banks and non-bank e-money issuers.
As of 2024, the system was processing about 1.5 million transactions daily and had the capacity to handle three times that volume.
Participation in TIPS is mandatory for inter-provider transactions, and 45 financial service providers were connected to the platform by the end of 2024.
The case study explains that BOT chose to develop the platform internally, rather than purchasing an external solution, to ensure efficiency, adaptability, sustainability, and control over future upgrades and support.
The platform was developed with financial support from FSDT and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, incorporating global best practices such as the Level One Project design principles and insights from other markets, including India and Jordan.
TIPS operates on a not-for-loss basis and includes features such as real-time processing, same-day settlement, transaction transparency, alias-based payment addressing, fraud prevention utilities, request-to-pay messaging, and transaction reversal functionality.
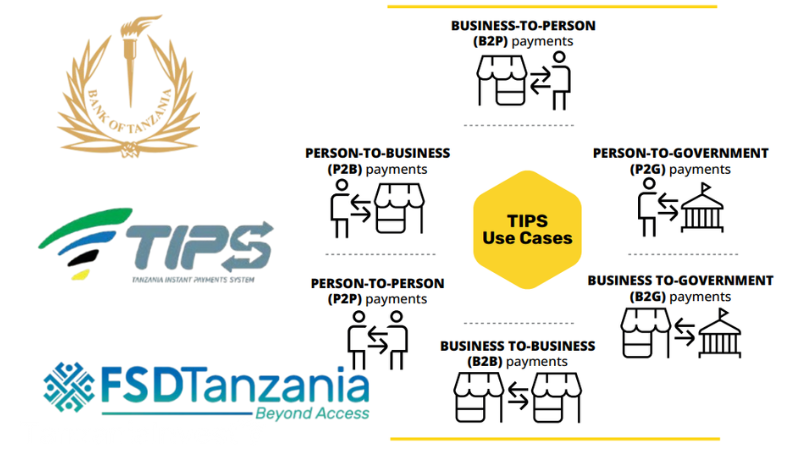
The system supports various use cases, including P2P, P2B, B2B, P2G, G2P, and B2G payments.
“TIPS is not only a strategic initiative under the National Financial Inclusion Framework (NFIF II) but also provides the rails for implementing the Tanzania Digital Economy Strategic Framework 2024–2034,” said Emmanuel M. Tutuba, Governor of the Bank of Tanzania.
“Through its inclusive design, TIPS provides an accessible, effective, inclusive, and affordable financial service infrastructure to all Tanzanians, which will stimulate economic growth and contribute to the strengthening of a competitive economy,” Tutuba added.
According to the study, the success of the system is attributed to inclusive stakeholder engagement, agile development methods, phased rollout, and strong internal capacity within BOT.
The case study also notes that TIPS is designed for future expansion, including cross-border transactions, and continues to evolve through new features and use cases based on user feedback and market needs.