A higher level of domestic debt in Tanzania is likely to be sustained without compromising the country’s economic growth.
This was indicated in the recently published Economic Development in Africa report, by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
Domestic debt is the amount of money raised by the Government in local currency and from its own residents to finance the country’s growth.
Tanzania Domestic Debt
The national borrowing strategy of Tanzania outlined in its 2002 budget guidelines initially focused on funding net budgetary deficits entirely from external sources.
In line with this strategy, the Government sought to limit net domestic financing to 1% of GDP, while maximizing external borrowing.
Tanzania’s domestic debt stood at USD918.2m at the end of 2000, which was one of the lowest among African countries.
This resulted from the national debt strategy of keeping domestic borrowing low, as well as a low national savings rate, and relatively underdeveloped debt and capital markets in the country.
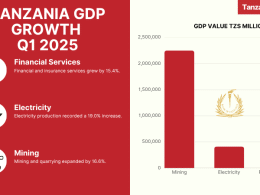
However, the value of domestic debt in Tanzania reached USD4.9b or 14% of GDP in 2014 due to growing financing needs of the Government and high infrastructure expenditure.
Tanzania Domestic Debt Expansion
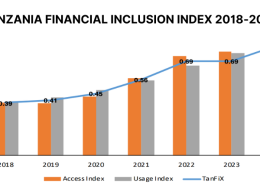
According to the report, there is greater scope for domestic debt to expand in Tanzania without crowding out bank lending to private sector investment and inducing inflationary pressures on the economy.
This is a result of Tanzania’s domestic debt being issued in the form of marketable securities (treasury bills), bearing positive real interest rates.
Tanzania has maintained positive real rates of return on its treasury securities since 2002.
Furthermore, Tanzania’s treasury bills are increasingly being issued to investors outside the banking system, particularly the pension and insurance sector.